Difference between revisions of "Numerical Solution Technique"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
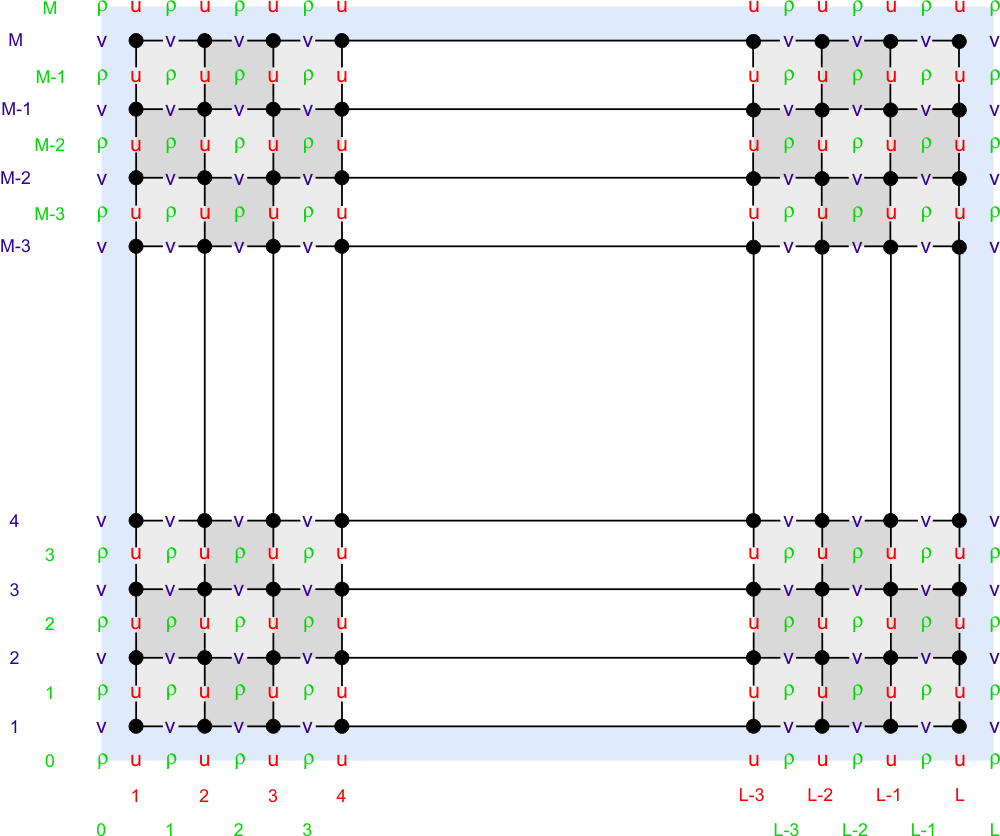
[[Image:staggered_grid_rho_cells.png|ROMS staggered rho grid]] | [[Image:staggered_grid_rho_cells.png|ROMS staggered rho grid]] | ||
The ROMS governing equations are discretized over variable topography using a stretched, terrain-following, vertical coordinate. As a result, each grid cell may have different level thickness (Hz) and volume. The model state variables are vertically staggered so that horizontal momentum (u,v), density, and tracers (active and passive) are located at the center of the grid cell. The vertical velocity (ω, w) and vertical mixing variables (Akt, Akv, etc) are located at the bottom and top faces of cell. See diagram below. | The ROMS governing equations are discretized over variable topography using a stretched, terrain-following, vertical coordinate. As a result, each grid cell may have different level thickness ([[Variables#Hz |Hz]]) and volume. The model state variables are vertically staggered so that horizontal momentum ([[Variables#u |u]], [[Variables#v |v]]), density, and tracers (active and passive) are located at the center of the grid cell. The vertical velocity ([[Variables#W |ω]], [[Variables#wvel |w]]) and vertical mixing variables ([[Variables#Akt |Akt]], [[Variables#Akv |Akv]], etc) are located at the bottom and top faces of cell. See diagram below. | ||
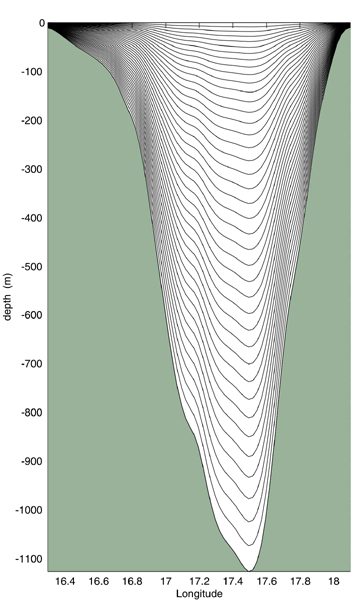
[[Image:vieste-dubrovnik.png|left|frame|<center>Vieste-Dubrovnik Transect</center>]] | [[Image:vieste-dubrovnik.png|left|frame|<center>Vieste-Dubrovnik Transect</center>]] | ||
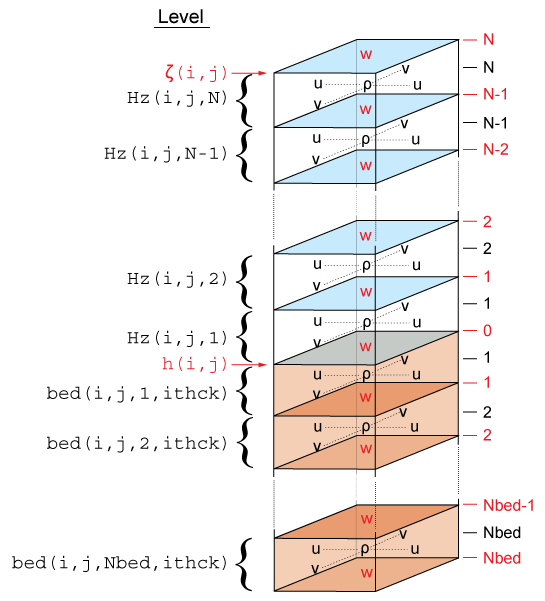
[[Image:vertical_grid.png|none|frame|<center>ROMS vertical grid</center>]] | [[Image:vertical_grid.png|none|frame|<center>ROMS vertical grid</center>]] | ||
<div style="clear:both;"></div> | <div style="clear:both;"></div> | ||
The total thickness of the water column is <span class="red">ζ(i,j)+h(i,j) | |||
</span>. The bathymetry ([[Variables#h |h]]) is usually time invariant. However, in sediment applications it changes with time when [[SED_MORPH]] is activated. At input and output, the bathymetry is always a positive quantity. However, the depths [[Variables#z_r |z_r(i,j,k)]] and [[Variables#z_w |z_w(i,j,k)]] of every grid cell are negative quantities in ROMS. | |||
==Time-Stepping== | ==Time-Stepping== | ||
Revision as of 21:00, 7 March 2008
Horizontal and Vertical Discretization
The ROMS governing equations are discretized over variable topography using a stretched, terrain-following, vertical coordinate. As a result, each grid cell may have different level thickness (Hz) and volume. The model state variables are vertically staggered so that horizontal momentum (u, v), density, and tracers (active and passive) are located at the center of the grid cell. The vertical velocity (ω, w) and vertical mixing variables (Akt, Akv, etc) are located at the bottom and top faces of cell. See diagram below.
The total thickness of the water column is ζ(i,j)+h(i,j) . The bathymetry (h) is usually time invariant. However, in sediment applications it changes with time when SED_MORPH is activated. At input and output, the bathymetry is always a positive quantity. However, the depths z_r(i,j,k) and z_w(i,j,k) of every grid cell are negative quantities in ROMS.