Difference between revisions of "Model Coupling ESMF"
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= | <div class="title">EARTH SYSTEM MODEL FRAMEWORK (ESMF)</div>__NOTOC__ | ||
<!-- Edit Template:Coupling_Examples_TOC to modify this Table of Contents--> | |||
<div style="float: left;margin: 0 20px 0 0;">{{ Coupling Examples TOC}}</div>__TOC__ | |||
<div style="clear: both"></div> | |||
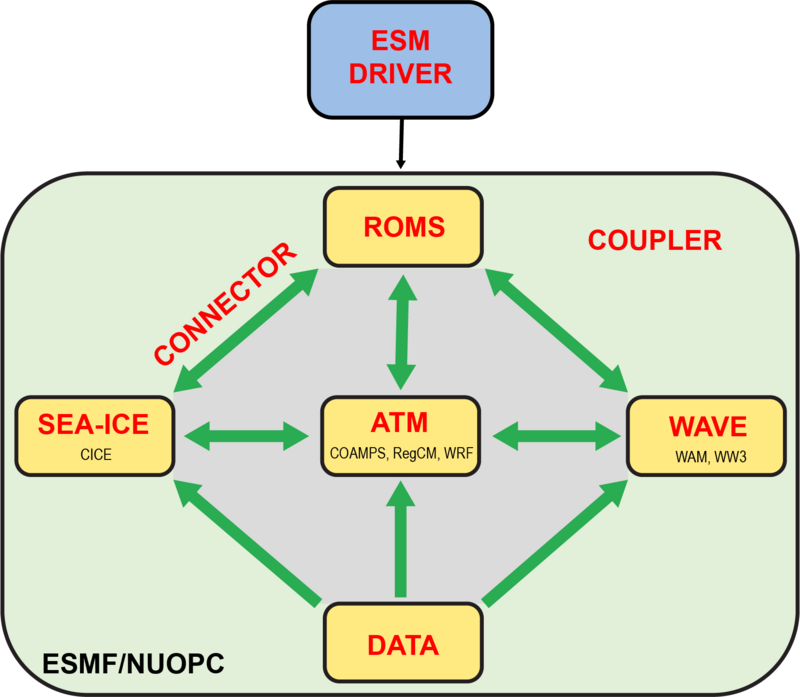
A prototype of the ROMS coupling framework based on the ESMF/NUOPC library is illustrated in Figure | ==Overview== | ||
Significant progress has been made over the past decade in the standardization of coupling tools without reducing model diversity through the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF; Collins ''et al.'', 2005) and the National Unified Operational Prediction Capability (NUOPC) consortia. The NUOPC layer is a simplified infrastructure on top of the ESMF library (version 7 or higher) that provides conventions and templates to facilitate easy coupling between Earth System Models (ESM). It consists of four components: (i) a driver, (ii) the models, (iii) mediators, and (iv) connectors. The driver controls the models, mediators, connectors, and coordinates tasks such as initialization and time stepping. The mediators are custom codes that facilitate the coupling of the models, and control tasks such as flux calculations, rescaling, and averaging. The connectors join ESM components and perform operations such as regridding between the source and destination fields when needed. While the NUOPC layer is available in ESMF version 7 of higher, ROMS coupling '''requires version 8 or higher''' because it uses the RunSequence input configuration script and uses version 8 features for nesting. | |||
The critical Fortran module that sits on top of each ESM is the so-called NUOPC <span class="red">cap</span> file. There is a separate <span class="red">cap</span> file for each coupled component, which, from the ROMS perspective, corresponds to the atmosphere, sea-ice, wave model, etc. Therefore, it is an abstract block that allows ROMS to communicate and exchange data seamlessly within the ESMF/NUOPC framework. The ROMS and other ESM grids may (and usually do) have a different geographical extent and horizontal resolution. So if, for example, the atmosphere component domain is larger than the ROMS domain, it is necessary to provide data from another source to the atmosphere model at all of the surface grid-points that lie outside the ROMS domain. Therefore, a DATA component and its <span class="red">cap</span> file is also required for most applications. In this case, SST is exported from ROMS and DATA to the atmosphere component which imports at melded SST field. | |||
The ROMS coupling interface with the ESMF/NUOPC library allows both driver and component methods of operation. In the driver method, it provides all the interfaces needed to couple to other ESM components including the executable driver, NUOPC-based generic ESM component services, model gridded components or NUOPC Model cap files, connectors between components for re-gridding source and destination fields, input scripts, and coupling metadata management. A NUOPC Model cap is a Fortran code layer that sits on top of the ESM component, making calls to the numerical kernel via the initialize, run, and finalize phases. Alternatively, in the component method, the NUOPC ROMS cap module is provided, and it can be adapted and incorporated into other NUOPC-based coupling systems, like the NOAA Environmental Modeling System (NEMS). | |||
[[Image:ROMS_Coupling.png|800px|center]] | |||
<center>'''''Figure 1:''''' ROMS driver mode ESMF/NUOPC coupling framework</center> | |||
A prototype of the ROMS coupling framework based on the ESMF/NUOPC library is illustrated in Figure 2 showing the Driver, Models, and Connectors. The Driver controls all the aspects of the coupling between the ESM components and their connections: configuration, initialization, time-stepping sequence, data exchanges, and termination. The Models are the gridded data and gridded geophysical numerical kernels wrapped into a NUOPC cap file interface. The Connectors between ESM components execute the remapping and regridding between the source and destination fields. The interpolation is usually linear with extrapolation support in the vicinity of masked grid cells. In this project, the coupling framework will include the Atmosphere Model (WRF), the Ocean Model (ROMS), and the Data Model since the grids are incongruent. The Data Model is needed because WRF requires sea surface temperature (SST) on those grid points not covered by ROMS (see Figure X). | |||
==Sequential Vs. Concurrent Mode== | |||
In sequential mode, all of the coupled model components are executed on all of the processors one after the other sequentially. In concurrent mode, each coupled model component executes on its own set of non-overlapping processors. | |||
==Regridding and Extrapolation Methods== | |||
Regridding interpolation methods between source and destination fields can be <span class="red">bilinear</span> or <span class="red">conservative</span>. Unmapped cells during regridding are usually located at land/sea boundaries. These unmapped cells can be mapped using the following methods: <span class="blue">nearest source to destination</span>, <span class="blue">nearest inverse distance average</span>, <span class="blue">creep fill at specified level</span>, or <span class="blue">two steps extrapolation</span> (Turuncoglu). | |||
<span class="blue">Indian Ocean Land/Sea Masks Mismatch??</span> | |||
<div class="box">! Cinfo(11) <span class="blue">Field regridding method from source to destination:</span><br />! '<span class="red">bilinear</span>' <span class="blue">=> bilinear interpolation</span><br />! '<span class="red">patch</span>' <span class="blue">=> high-order patch recovery</span><br />! '<span class="red">conservative1</span>' <span class="blue">=> first-order conservative</span><br />! '<span class="red">conservative2</span>' <span class="blue">=> second-order conservative</span><br />! '<span class="red">nearest</span>' <span class="blue">=> nearest neighbor interpolation</span><br />! Cinfo(12) <span class="blue">Field extrapolation method for unmapped points:</span><br />! '<span class="red">none</span>' <span class="blue">=> no extrapolation</span><br />! '<span class="red">nearest</span>' <span class="blue">=> nearest source to destination</span><br />! '<span class="red">idavg</span>' <span class="blue">=> nearest inverse distance average</span><br />! '<span class="red">creep</span>' <span class="blue">=> creep fill at specified level</span><br />! '<span class="red">2steps</span>' <span class="blue">=> Turuncoglu's 2 steps extrapolation</span><br /><br />'<span class="red">SST</span>'<br /> '<span class="red">sea_surface_temperature</span>' <span class="blue">! standard name</span><br /> '<span class="red">sea surface temperature</span>'<br /> '<span class="red">t(:,:,N,itemp)</span>', '<span class="red">ROMS</span>' <span class="blue">! source variable, ROMS</span><br /> '<span class="red">C</span>' <span class="blue">! source units</span><br /> '<span class="red">Center</span>' <span class="blue">! source grid-cell</span><br /> '<span class="red">sst</span>', '<span class="red">WRF</span>' <span class="blue">! destination variable, WRF</span><br /> '<span class="red">K</span>' <span class="blue">! destination units</span><br /> '<span class="red">Center</span>' <span class="blue">! destination grid-cell</span><br /> '<span class="red">SST</span>' <span class="blue">! DATA Model file variable</span><br /> '<span class="red">bilinear</span>' <span class="blue">!</span> <span class="violet">regridding method</span><br /> '<span class="red">nearest</span>' <span class="blue">!</span> <span class="violet">unmapped extrapolation method</span><br /> <span class="red">.TRUE.</span> <span class="blue">! connected to coupler</span><br /> <span class="red">.FALSE.</span> <span class="blue">! debug write into a NetCDF file</span><br /> <span class="red">273.15d0</span> <span class="blue">! importing add offset</span><br /> <span class="red">1.0d0</span> <span class="blue">! importing scale</span></div> | |||
<div class="box">'<span class="red">dSST</span>'<br /> '<span class="red">sea_surface_temperature_data</span>' <span class="blue">! standard name</span><br /> '<span class="red">sea surface temperature data</span>'<br /> '<span class="red">temperature</span>', '<span class="red">HyCOM</span>' <span class="blue">! source variable, DATA</span><br /> '<span class="red">C</span>' <span class="blue">! source units</span><br /> '<span class="red">Center</span>' <span class="blue">! source grid-cell</span><br /> '<span class="red">sst</span>', '<span class="red">WRF</span>' <span class="blue">! destination variable, WRF</span><br /> '<span class="red">K</span>' <span class="blue">! destination units</span><br /> '<span class="red">Center</span>' <span class="blue">! destination grid-cell</span><br /> '<span class="red">temperature</span>' <span class="blue">! DATA field and time variables</span><br /> '<span class="red">bilinear</span>' <span class="blue">!</span> <span class="violet">regridding method</span><br /> '<span class="red">nearest</span>' <span class="blue">!</span> <span class="violet">unmapped extrapolation method</span><br /> <span class="red">.TRUE.</span> <span class="blue">! connected to coupler</span><br /> <span class="red">.FALSE.</span> <span class="blue">! debug write into a NetCDF file</span><br /> <span class="red">273.15d0</span> <span class="blue">! importing add offset</span><br /> <span class="red">1.0d0</span> <span class="blue">! importing scale</span></div> | |||
==Explicit Vs. Semi-Implicit Run Sequence== | |||
{| | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|[[Image:DATA-ATM-ROMS_Explicit_Coupling.png|550px]] | |||
|style="width:10px;"| | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|[[Image:DATA-ATM-ROMS_Semi-Implicit_Avg_Coupling.png|550px]] | |||
|- | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Explicit''' | |||
|style="width:10px;"| | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Semi-Implicit, ATM Average''' | |||
|- | |||
|style="padding:0px 15px 0px 15px;background-color:#FFE699;"|<div class="box"><span class="blue"># Hurricane Irene Application (single time loop)</span><br /><br />runSeq::<br /> @240 <span class="blue"># timeStep = 4 min interval</span><br /> <span class="red">DATA</span> -> <span class="red">WRF</span> <span class="blue"># DATA to WRF connector</span> [[Image:bw1.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">DATA</span><br /> <span class="red">WRF</span> -> <span class="red">ROMS</span> <span class="blue"># WRF to ROMS connector</span> [[Image:bw2.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">ROMS</span> -> <span class="red">WRF</span> <span class="blue"># ROMS to WRF connector</span> [[Image:bw3.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">WRF</span> [[Image:bw4.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">ROMS</span> [[Image:bw5.png|12px]]<br /> @<br />::</div> | |||
|style="width:10px;"| | |||
|style="padding:0px 15px 0px 15px;background-color:#FFE699;"|<div class="box"><span class="blue"># Hurricane Irene Application (single time loop)</span><br /><br />runSeq::<br /> @* <span class="blue"># timeStep = wildcard (*)</span><br /> <span class="red">DATA</span> -> <span class="red">WRF</span> <span class="blue"># DATA to WRF connector</span> [[Image:bw1.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">DATA</span><br /> <span class="red">ROMS</span> -> <span class="red">WRF</span> <span class="blue"># ROMS to WRF connector</span> [[Image:bw2.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">WRF</span> [[Image:bw3.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">WRF</span> -> <span class="red">ROMS</span> <span class="blue"># WRF to ROMS connector</span> [[Image:bw4.png|12px]]<br /> <span class="red">ROMS</span> [[Image:bw5.png|12px]]<br /> @<br />::</div> | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Atmosphere exports instantaneous fields''' | |||
|style="width:10px;"| | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Atmosphere exports time-averaged fields | |||
<span class="red">(Recommended for Conservation)</span> | |||
''' | |||
|} | |||
===Semi-Implicit Algorithm Details=== | |||
The following diagram shows the sequence of exchanges in a <span class="green">DATA</span>'''-'''<span class="red">ATM</span>'''-'''<span class="blue">ROMS</span> coupling system. The connector <span class="blue">ROMS</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span> is explicit, whereas the connector <span class="red">ATM</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="blue">ROMS</span> is semi-implicit. Usually, the timestep of the atmosphere kernel is smaller than that of the ocean. Thus, <span class="red">ATM</span> export fields are time-averaged over the coupling interval, which is the same as the <span class="blue">ROMS</span> timestep. Currently, in our coupling system, we have '''NUOPC''' cap files for <span class="red">COAMPS</span> and <span class="red">WRF</span> replacing the generic <span class="red">ATM</span> label. | |||
[[Image:DATA-ATM-ROMS_Semi-Implicit_Avg_Coupling_Frame_5.png|550px]] | |||
That is, the detailed sequence of routines called is as follows: | |||
<div class="box"> '''ESM_SetServices'''<br /><br /> '''ESM_SetModelServices'''<br /><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetServices</span><br /><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetServices</span><br /><br /> <span class="green">DATA_SetServices</span><br /><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_SetServices</span> set interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="blue">ROMS</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_SetServices</span> set interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="red">ATM</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="blue">ROMS</span><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_SetServices</span> set interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="green">DATA</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span><br /><br /> '''ESM_SetRunSequence'''<br /><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetInitializeP1</span><br /><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetInitializeP1</span><br /><br /> <span class="green">DATA_SetInitializeP1</span><br /><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetInitializeP2</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_Initialize</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetGridArrays</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetStates</span><br /><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetInitializeP2</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_Initialize</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetGridArrays</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetStates</span><br /><br /> <span class="green">DATA_SetInitializeP2</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_Initialize</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_multifile</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_checkfile</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_inquiry</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_ncvarcoords</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_ncread</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_SetGridArrays</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_SetStates</span><br /><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ComputeRH</span> compute interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="blue">ROMS</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ComputeRH</span> compute interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="red">ATM</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="blue">ROMS</span><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ComputeRH</span> compute interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="green">DATA</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span><br /><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetClock</span><br /><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetClock</span><br /><br /> <span class="green">DATA_SetClock</span><br /><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_DataInit</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_Export</span><br /><br /> <span class="red">ATM_DataInit</span><br /><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ExecuteRH</span> apply interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="green">DATA</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span><br /><br /> <span class="green">DATA_ModelAdvance</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_ncread</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_Export</span><br /> <span class="green">DATA_TimeInterp</span><br /><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ExecuteRH</span> apply interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="blue">ROMS</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span><br /><br /> <span class="red">ATM_SetRunClock</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_CheckImport</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_ModelAdvance</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_Import</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_ProcessImport</span><br /> <span class="red">ATM_Export</span><br /><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ExecuteRH</span> apply interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="red">ATM</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="blue">ROMS</span><br /><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_SetRunClock</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_CheckImport</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_ModelAdvance</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_Import</span><br /> <span class="blue">ROMS_Export</span><br /><br /> <span class="darkTurquoise">Coupler_ExecuteRH</span> apply interpolation '''RouteHandle''' <span class="green">DATA</span>'''-TO-'''<span class="red">ATM</span></div> | |||
==Coupling with Nested Grids== | |||
<center>[[Image:Coupling_with_Nested_Grids.png|800px]] | |||
{|style="width:800px;background-color:#FFE699;padding:10px;" | |||
|Component | |||
|Grid | |||
|CoupledSet | |||
|ImportState | |||
|ExportState | |||
|ConnectedTo | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="6"|<nowiki>-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
|<span class="red">ROMS</span> | |||
|1 | |||
|<span class="red">ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Import_ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Export_ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="red">COAMPS</span> | |||
|- | |||
|<span class="red">COAMPS</span> | |||
|1 | |||
|<span class="red">ESM_01</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Import_ESM_01</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Export_ESM_01</span> | |||
|<span class="red">DATA</span> | |||
|- | |||
|<span class="red">COAMPS</span> | |||
|2 | |||
|<span class="red">ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Import_ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Export_ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="red">ROMS</span>''', '''<span class="red">DATA</span> | |||
|- | |||
|<span class="red">DATA</span> | |||
|1 | |||
|<span class="red">ESM_01</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">NONE</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Export_ESM_01</span> | |||
|<span class="red">COAMPS</span> | |||
|- | |||
|<span class="red">DATA</span> | |||
|1 | |||
|<span class="red">ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">NONE</span> | |||
|<span class="forestGreen">Export_ESM_02</span> | |||
|<span class="red">COAMPS</span> | |||
|}</center> | |||
* Active coupled Earth System Models (ESM) switches. If a component is nested, each grid is considered an independent component. Specify which nested grids are coupled. The first grid of active ESM components must always be coupled.<div class="box"> [[Variables#IsActive|IsActive(roms)]] = T ! ROMS ([[Variables#NgridsR|NgridsR]])<br /> [[Variables#IsActive|IsActive(atmos)]] = T ! atmosphere model ([[Variables#NgridsA|NgridsA]])<br /> [[Variables#IsActive|IsActive(seaice)]] = F ! seaice model ([[Variables#NgridsI|NgridsI]])<br /> [[Variables#IsActive|IsActive(waves)]] = F ! wave model ([[Variables#NgridsW|NgridsW]])<br /> [[Variables#IsActive|IsActive(data)]] = T ! DATA model</div> | |||
* Set which ESM components are connected to the ocean component (ROMS) during coupling. If ROMS has nested grids, indicate which grids are connected to the other ESM components, [1:[[Variables#NgridsR|NgridsR]]] expected.<div class="box"> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(ATM2OCN)]] == T ! atmosphere -> ROMS connected<br /> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(ICE2OCN)]] == F ! seaice -> ROMS connected<br /> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(WAV2OCN)]] == F ! wave -> ROMS connected<br /> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(DAT2OCN)]] == F ! DATA -> ROMS connected</div> | |||
* Set which ESM components are connected to the atmosphere component during coupling. If the atmosphere component has nested grids, indicate which grids are connected to the other ESM components, [1:[[Variables#NgridsA|NgridsA]]] expected.<div class="box"> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(OCN2ATM)]] == F T ! ROMS -> atmosphere connected<br /> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(ICE2ATM)]] == F ! seaice -> atmosphere connected<br /> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(WAV2ATM)]] == F ! wave -> atmosphere connected<br /> [[Variables#Coupled|Coupled(DAT2ATM)]] == T T ! DATA -> atmosphere connected</div> | |||
Latest revision as of 16:23, 27 April 2022
| Coupling Examples TOC |
|---|
| 2. Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF/NUOPC) |
| a. Test Case: Hurricane Irene |
| b. Test Case: Hurricane Sandy |
| c. Test Case: California Current System |
| 3. Model Coupling Toolkit (MCT) |
Overview
Significant progress has been made over the past decade in the standardization of coupling tools without reducing model diversity through the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF; Collins et al., 2005) and the National Unified Operational Prediction Capability (NUOPC) consortia. The NUOPC layer is a simplified infrastructure on top of the ESMF library (version 7 or higher) that provides conventions and templates to facilitate easy coupling between Earth System Models (ESM). It consists of four components: (i) a driver, (ii) the models, (iii) mediators, and (iv) connectors. The driver controls the models, mediators, connectors, and coordinates tasks such as initialization and time stepping. The mediators are custom codes that facilitate the coupling of the models, and control tasks such as flux calculations, rescaling, and averaging. The connectors join ESM components and perform operations such as regridding between the source and destination fields when needed. While the NUOPC layer is available in ESMF version 7 of higher, ROMS coupling requires version 8 or higher because it uses the RunSequence input configuration script and uses version 8 features for nesting.
The critical Fortran module that sits on top of each ESM is the so-called NUOPC cap file. There is a separate cap file for each coupled component, which, from the ROMS perspective, corresponds to the atmosphere, sea-ice, wave model, etc. Therefore, it is an abstract block that allows ROMS to communicate and exchange data seamlessly within the ESMF/NUOPC framework. The ROMS and other ESM grids may (and usually do) have a different geographical extent and horizontal resolution. So if, for example, the atmosphere component domain is larger than the ROMS domain, it is necessary to provide data from another source to the atmosphere model at all of the surface grid-points that lie outside the ROMS domain. Therefore, a DATA component and its cap file is also required for most applications. In this case, SST is exported from ROMS and DATA to the atmosphere component which imports at melded SST field.
The ROMS coupling interface with the ESMF/NUOPC library allows both driver and component methods of operation. In the driver method, it provides all the interfaces needed to couple to other ESM components including the executable driver, NUOPC-based generic ESM component services, model gridded components or NUOPC Model cap files, connectors between components for re-gridding source and destination fields, input scripts, and coupling metadata management. A NUOPC Model cap is a Fortran code layer that sits on top of the ESM component, making calls to the numerical kernel via the initialize, run, and finalize phases. Alternatively, in the component method, the NUOPC ROMS cap module is provided, and it can be adapted and incorporated into other NUOPC-based coupling systems, like the NOAA Environmental Modeling System (NEMS).
A prototype of the ROMS coupling framework based on the ESMF/NUOPC library is illustrated in Figure 2 showing the Driver, Models, and Connectors. The Driver controls all the aspects of the coupling between the ESM components and their connections: configuration, initialization, time-stepping sequence, data exchanges, and termination. The Models are the gridded data and gridded geophysical numerical kernels wrapped into a NUOPC cap file interface. The Connectors between ESM components execute the remapping and regridding between the source and destination fields. The interpolation is usually linear with extrapolation support in the vicinity of masked grid cells. In this project, the coupling framework will include the Atmosphere Model (WRF), the Ocean Model (ROMS), and the Data Model since the grids are incongruent. The Data Model is needed because WRF requires sea surface temperature (SST) on those grid points not covered by ROMS (see Figure X).
Sequential Vs. Concurrent Mode
In sequential mode, all of the coupled model components are executed on all of the processors one after the other sequentially. In concurrent mode, each coupled model component executes on its own set of non-overlapping processors.
Regridding and Extrapolation Methods
Regridding interpolation methods between source and destination fields can be bilinear or conservative. Unmapped cells during regridding are usually located at land/sea boundaries. These unmapped cells can be mapped using the following methods: nearest source to destination, nearest inverse distance average, creep fill at specified level, or two steps extrapolation (Turuncoglu).
Indian Ocean Land/Sea Masks Mismatch??
! 'bilinear' => bilinear interpolation
! 'patch' => high-order patch recovery
! 'conservative1' => first-order conservative
! 'conservative2' => second-order conservative
! 'nearest' => nearest neighbor interpolation
! Cinfo(12) Field extrapolation method for unmapped points:
! 'none' => no extrapolation
! 'nearest' => nearest source to destination
! 'idavg' => nearest inverse distance average
! 'creep' => creep fill at specified level
! '2steps' => Turuncoglu's 2 steps extrapolation
'SST'
'sea_surface_temperature' ! standard name
'sea surface temperature'
't(:,:,N,itemp)', 'ROMS' ! source variable, ROMS
'C' ! source units
'Center' ! source grid-cell
'sst', 'WRF' ! destination variable, WRF
'K' ! destination units
'Center' ! destination grid-cell
'SST' ! DATA Model file variable
'bilinear' ! regridding method
'nearest' ! unmapped extrapolation method
.TRUE. ! connected to coupler
.FALSE. ! debug write into a NetCDF file
273.15d0 ! importing add offset
1.0d0 ! importing scale
'sea_surface_temperature_data' ! standard name
'sea surface temperature data'
'temperature', 'HyCOM' ! source variable, DATA
'C' ! source units
'Center' ! source grid-cell
'sst', 'WRF' ! destination variable, WRF
'K' ! destination units
'Center' ! destination grid-cell
'temperature' ! DATA field and time variables
'bilinear' ! regridding method
'nearest' ! unmapped extrapolation method
.TRUE. ! connected to coupler
.FALSE. ! debug write into a NetCDF file
273.15d0 ! importing add offset
1.0d0 ! importing scale
Explicit Vs. Semi-Implicit Run Sequence

|

| |
| Explicit | Semi-Implicit, ATM Average | |
| Atmosphere exports instantaneous fields | Atmosphere exports time-averaged fields
(Recommended for Conservation) |
Semi-Implicit Algorithm Details
The following diagram shows the sequence of exchanges in a DATA-ATM-ROMS coupling system. The connector ROMS-TO-ATM is explicit, whereas the connector ATM-TO-ROMS is semi-implicit. Usually, the timestep of the atmosphere kernel is smaller than that of the ocean. Thus, ATM export fields are time-averaged over the coupling interval, which is the same as the ROMS timestep. Currently, in our coupling system, we have NUOPC cap files for COAMPS and WRF replacing the generic ATM label.
That is, the detailed sequence of routines called is as follows:
ESM_SetModelServices
ROMS_SetServices
ATM_SetServices
DATA_SetServices
Coupler_SetServices set interpolation RouteHandle ROMS-TO-ATM
Coupler_SetServices set interpolation RouteHandle ATM-TO-ROMS
Coupler_SetServices set interpolation RouteHandle DATA-TO-ATM
ESM_SetRunSequence
ROMS_SetInitializeP1
ATM_SetInitializeP1
DATA_SetInitializeP1
ROMS_SetInitializeP2
ROMS_Initialize
ROMS_SetGridArrays
ROMS_SetStates
ATM_SetInitializeP2
ATM_Initialize
ATM_SetGridArrays
ATM_SetStates
DATA_SetInitializeP2
DATA_Initialize
DATA_multifile
DATA_checkfile
DATA_inquiry
DATA_ncvarcoords
DATA_ncread
DATA_SetGridArrays
DATA_SetStates
Coupler_ComputeRH compute interpolation RouteHandle ROMS-TO-ATM
Coupler_ComputeRH compute interpolation RouteHandle ATM-TO-ROMS
Coupler_ComputeRH compute interpolation RouteHandle DATA-TO-ATM
ROMS_SetClock
ATM_SetClock
DATA_SetClock
ROMS_DataInit
ROMS_Export
ATM_DataInit
Coupler_ExecuteRH apply interpolation RouteHandle DATA-TO-ATM
DATA_ModelAdvance
DATA_ncread
DATA_Export
DATA_TimeInterp
Coupler_ExecuteRH apply interpolation RouteHandle ROMS-TO-ATM
ATM_SetRunClock
ATM_CheckImport
ATM_ModelAdvance
ATM_Import
ATM_ProcessImport
ATM_Export
Coupler_ExecuteRH apply interpolation RouteHandle ATM-TO-ROMS
ROMS_SetRunClock
ROMS_CheckImport
ROMS_ModelAdvance
ROMS_Import
ROMS_Export
Coupler_ExecuteRH apply interpolation RouteHandle DATA-TO-ATM
Coupling with Nested Grids

| Component | Grid | CoupledSet | ImportState | ExportState | ConnectedTo |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||||
| ROMS | 1 | ESM_02 | Import_ESM_02 | Export_ESM_02 | COAMPS |
| COAMPS | 1 | ESM_01 | Import_ESM_01 | Export_ESM_01 | DATA |
| COAMPS | 2 | ESM_02 | Import_ESM_02 | Export_ESM_02 | ROMS, DATA |
| DATA | 1 | ESM_01 | NONE | Export_ESM_01 | COAMPS |
| DATA | 1 | ESM_02 | NONE | Export_ESM_02 | COAMPS |
- Active coupled Earth System Models (ESM) switches. If a component is nested, each grid is considered an independent component. Specify which nested grids are coupled. The first grid of active ESM components must always be coupled.IsActive(roms) = T ! ROMS (NgridsR)
IsActive(atmos) = T ! atmosphere model (NgridsA)
IsActive(seaice) = F ! seaice model (NgridsI)
IsActive(waves) = F ! wave model (NgridsW)
IsActive(data) = T ! DATA model
- Set which ESM components are connected to the ocean component (ROMS) during coupling. If ROMS has nested grids, indicate which grids are connected to the other ESM components, [1:NgridsR] expected.Coupled(ATM2OCN) == T ! atmosphere -> ROMS connected
Coupled(ICE2OCN) == F ! seaice -> ROMS connected
Coupled(WAV2OCN) == F ! wave -> ROMS connected
Coupled(DAT2OCN) == F ! DATA -> ROMS connected
- Set which ESM components are connected to the atmosphere component during coupling. If the atmosphere component has nested grids, indicate which grids are connected to the other ESM components, [1:NgridsA] expected.Coupled(OCN2ATM) == F T ! ROMS -> atmosphere connected
Coupled(ICE2ATM) == F ! seaice -> atmosphere connected
Coupled(WAV2ATM) == F ! wave -> atmosphere connected
Coupled(DAT2ATM) == T T ! DATA -> atmosphere connected